In industrial and electrical fields, fire safety is crucial. Flame retardant cable ties, as a specialized type with flame retardant properties, are more effective than standard cable ties at handling high temperatures and fire risks, thereby ensuring safety. This article will provide a detailed introduction to the definition, material characteristics, and advantages of flame retardant cable ties, along with their applications, testing standards, testing methods, and evaluation criteria.
What Are Flame Retardant Cable Ties

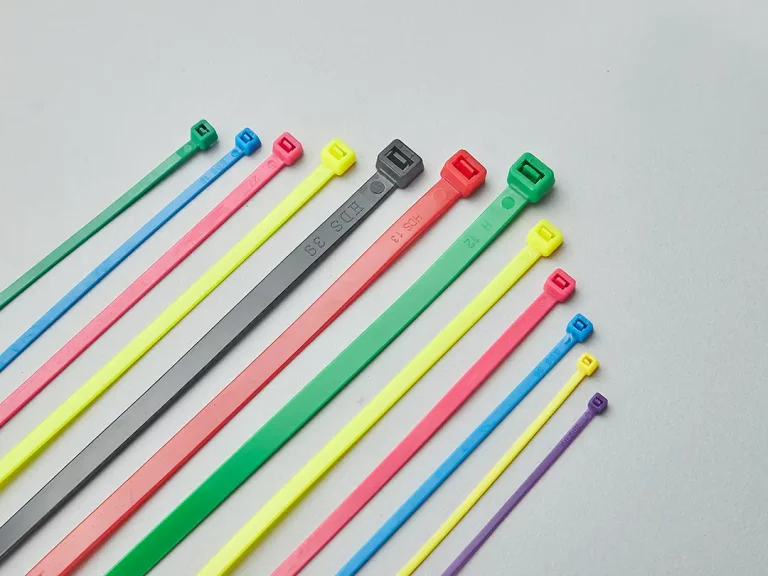
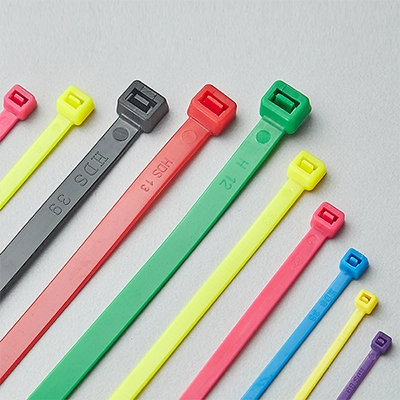
Flame retardant cable ties are made from PA66V0, for example, Zytel® FR7025V0F, with excellent flame retardant properties. In high-temperature or open flame environments, these ties can effectively prevent fire spread, reducing fire risks.
They are mainly used in industrial, electrical, and construction fields where strict fire safety is required to ensure a safe and stable environment. Additionally, as shown in the image, flame retardant cable ties are less translucent and appear more milky white than standard cable ties.
Characteristics and Advantages of Flame Retardant Cable Ties
Flame retardant cable ties are made from flame-resistant nylon 66. Here are their main characteristics and advantages:
Characteristics
Flame Retardancy: Made from UL94-V0 PA66, which can effectively slow down the burning speed and prevent fire from spreading in high-temperature or open fire environments.
High-Temperature Resistance: This material remains stable and does not deform easily in high-temperature environments.
Chemical Resistance: Flame retardant cable ties resist various chemicals, making them suitable for severe environments.
Advantages
Standard nylon cable ties have a flame retardant rating of UL94-V2, while flame retardant cable ties can achieve UL94-V0. This means flame retardant cable ties can quickly self-extinguish in fire, completely preventing fire spreading and significantly reducing fire risks. Therefore, they are widely used in industrial, electrical, and construction fields requiring strict fire prevention measures. For more information about UL94 flammability ratings, refer to the article “UL94 Flammability: An Clear Guide for Cable Ties“.
Applications of Flame Retardant Cable Ties
Flame retardant cable ties are widely used in fields that require strict fire safety measures, such as the following key applications:
- Electrical Equipment: Flame retardant cable ties are used to secure and bundle cables and wires, preventing electrical fires.
- Construction Sites: On construction sites, they are used to bundle and secure various materials and equipment, preventing fire from spreading.
- Data Centers: In data centers and server rooms, flame-retardant cable ties are used to manage and bundle abundant cables, protecting equipment from fire damage.
- Other High-Risk Environments: In high-risk environments such as chemical plants and oil fields, flame retardant cable ties ensure the safety of equipment and pipelines in high-temperature or fire-prone conditions.
Testing Standards for Flame Retardant Cable Ties
The flammability of flame retardant cable ties is primarily evaluated with the UL94 standard, specifically Section 8 of UL94-2023. UL94 is a crucial standard to assess the flame retardancy of plastic materials under vertical and horizontal burning conditions.
For detailed content of the standard, refer to the article above “UL94 Flammability: An Clear Guide for Cable Ties”.
Testing Methods for Flame Retardant Cable Ties
Sample Requirements
Testing the flammability of flame-retardant cable ties is different from other tests required for nylon cable ties. According to UL94 requirements, the test samples must be of specific dimensions. The specific requirements are as follows:
- Sample Size: 125×13×(0.025~13) mm
- Sample Quantity: 20 pieces
- Sample Condition: Samples must be regular, flat, and no visible defects
Testing Requirements
UL94 flame retardant testing is not completed in a single step. Samples must undergo two tests under different conditions to ensure the reliability of their flame-retardant properties. Both tests must be passed for the sample to be considered qualified:
- Testing under Normal Conditions: (23±2)℃, (50±5)%RH, for 48 hours
- Testing under Heat-Aged Conditions: (70±2)℃ for 168 hours of heat aging, followed by drying at (23±2)℃ for 4 hours
Vertical Burning Test
The sample is fixed in a burning test apparatus and subjected to two flame ignitions, each lasting 10 seconds. The self-extinguishing time of the sample, the presence of any dripping material, and whether the dripped material ignites the cotton underneath are recorded.
Criteria for UL94-V0 Flame Retardant Cable Ties
| Test criteria | V-0 | V-1 | V-2 |
| Total flaming comments for each specimen, t1 and t2 | ≤10s | ≤30s | ≤30s |
| Total flaming combustion for all 5 specimens (t1+t2 ) | ≤50s | ≤250s | ≤250s |
| Flaming and glowing combustion for each specimen after the second burner flame application (t2+t3) | ≤30s | ≤60s | ≤60s |
| Glowing or flaming combustion of any specimen to holding clamp | No | No | No |
| Cotton ignited by flaming drips from any specimen | No | No | Yes |
HUADA Flame Retardant Cable Ties
HUADA flame retardant cable ties Meet UL94-V0 Standards: Test Results Below
| Treatment condition | Normal condition: (23±2)℃, (50±5)%RH, 48h | Heat aging in (70±2)℃ for 168 h, then dried in (23±2)℃ for 4h | ||||||||
| Specimen test | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Flaming combustion after first burner flame,t1(s) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Flaming combustion after second burner flame,t2(s) | 0 | 0 | 1.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Glowing combustion after second burner flame,t3(s) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total flaming combustion,t1+t2(s) | 1.3 | 0 | ||||||||
| Flaming and glowing combustion for each specimen after the second burner flame application, t2+t3(s) | 0 | 0 | 1.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Glowing or flaming combustion of any specimen to holding clamp | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Cotton ignited by flaming drips from any specimen | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |