What is the difference between Nylon 66 Cable Ties and Nylon 6 Cable Ties? Many people raise this question when choosing the material for nylon cable ties. Despite both being nylon, Nylon 66 and Nylon 6 have distinct differences in structure, performance, and applications. This article will provide a detailed comparison between Nylon 66 cable tie and Nylon 6 cable tie, helping you select the most suitable cable tie for your needs.
1. Structure
Nylon 66 (PA66) and Nylon 6 (PA6) might have similar names, but their molecular structures are different, which affects the performance of cable ties significantly.
Nylon 66 (PA66) is made from adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine through the polycondensation reaction, which consists of two different monomers. This structure results in longer molecular chains and higher crystallinity, providing greater rigidity and strength so that it can keep shape and strength even at high temperatures.
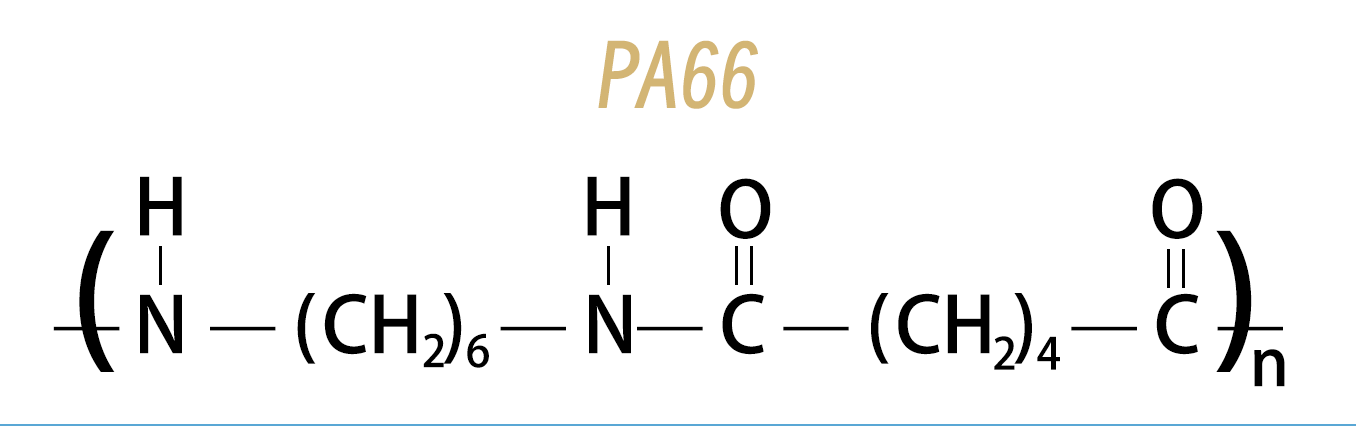
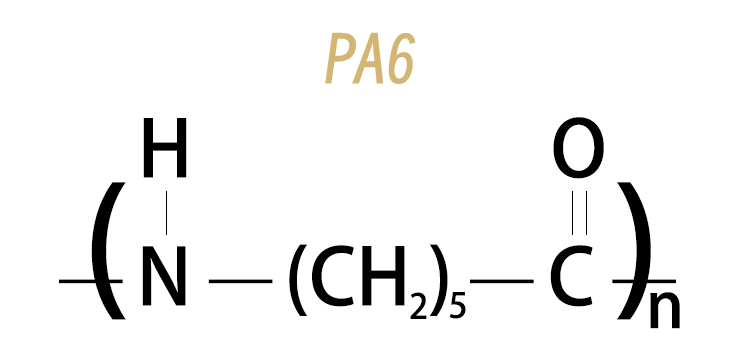
Nylon 6 (PA6) is a kind of polyamide made from caprolactam through the ring-opening polymerization with a single monomer. This structure results in shorter molecular chains and lower crystallinity so that it has better flexibility and impact resistance, and easier injection molding.
2. Performance
1. Thermal Stability
The thermal performance of cable ties can be evaluated based on their melting and glass transition temperatures.
1.1 Melting Point
The melting point is the temperature at which a solid substance transitions to a liquid state
- PA6: The melting point of PA6 is approximately 220℃.
- PA66: The melting point of PA66 is approximately 260℃.
1.2 Glass Transition Temperature
The glass transition temperature (Tg) is the temperature at which a polymer transitions from a hard and brittle state (glassy state) to a soft and flexible state (rubbery state).
- PA6: The glass transition temperature of PA6 is approximately 50℃.
- PA66: The glass transition temperature of PA66 is approximately 70℃.
Summary: Regarding thermal stability, PA6 and PA66 exhibit different behaviors. PA66 has a higher crystallinity and greater amide bonds, resulting in stronger intermolecular interactions. Consequently, PA66 has a higher melting point and glass transition temperature compared to PA6. This means that PA66 can maintain its structure and stability at higher temperatures, offering better thermal stability. You can refer to the article High-Temp Testing: Nylon 6 vs. Nylon 66 Cable Ties, then you will have a more comprehensive understanding.
2. Mechanical Performance
- PA6 has a higher elongation at break, meaning it is more ductile and better at absorbing impact forces. This makes PA6 suitable for applications requiring flexibility and impact resistance.
- PA66, with its more orderly crystal structure, offers better stiffness and tensile strength compared to PA6. This makes PA66 ideal for applications requiring high tensile strength and rigidity.
3. Creep Performance
Creep performance refers to the ability of a material to resist deformation under long-term load. The difference in creep performance between PA6 and PA66 affects their longevity in applications under continuous stress.
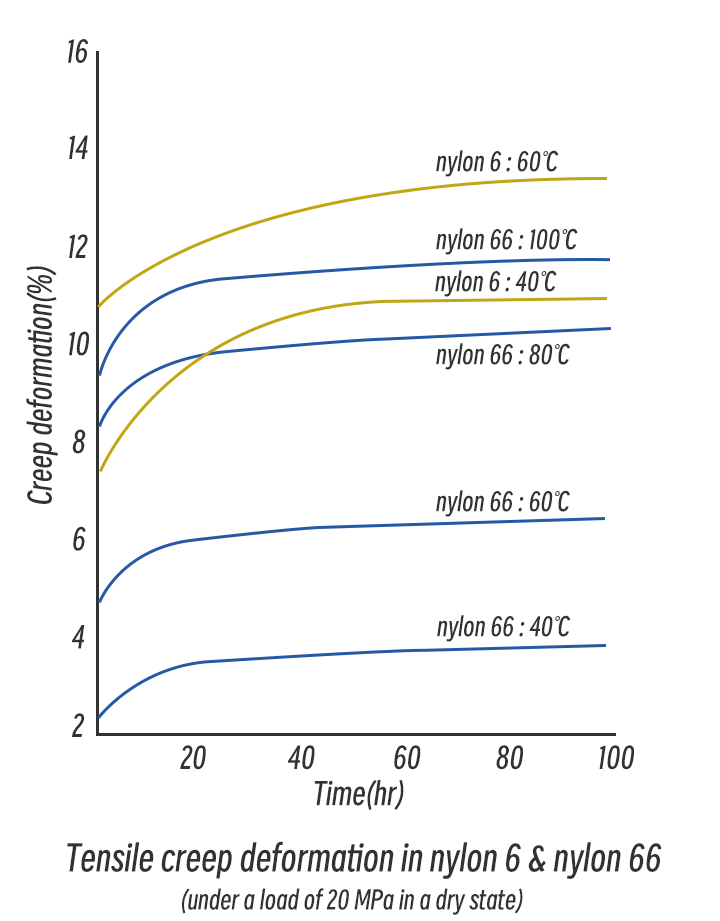
- PA66 exhibits better creep performance, meaning it deforms less under long-term load and maintains good shape stability. This is due to PA66’s higher stiffness and stronger intermolecular forces, making it less prone to deformation under sustained pressure.
- PA6 has relatively poor creep performance. Under long-term load, PA6 is more likely to deform.
4. Chemical Resistance
- PA6 has good resistance to many chemicals, including oils, greases, and aliphatic hydrocarbons. However, in extreme chemical environments, its performance is not as good as PA66.
- PA66 has better resistance to solvents and chemicals, thanks to its higher number of amide bonds in the polymer chain, enhancing its chemical resistance. This makes PA66 suitable for harsh chemical environments.
5. Moisture Absorption
Moisture absorption affects the physical properties and dimensional stability of nylon materials. For more detailed information on this topic, you can refer to the article Water Absorption in Cable Ties.
- PA6 has higher moisture absorption, which can lead to dimensional changes and a reduction in mechanical properties in high-humidity environments.
- PA66 has lower moisture absorption compared to PA6, making it more stable and reliable in humid conditions.
Summary
In summary, PA6 and PA66 have different strengths and weaknesses. PA6 offers better flexibility and impact resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring these properties. However, its higher moisture absorption and poorer creep performance limit its use in some environments. PA66, with its superior thermal stability, stiffness, tensile strength, creep performance, and chemical resistance, is better suited for high-strength and high-temperature applications, as well as harsh chemical environments.
3. Applications
The most notable differences between nylon 6 cable ties and nylon 66 cable ties lie in their mechanical and thermal properties. Additionally, cost-efficiency is an important factor to consider, as PA66 is significantly more expensive than PA6. Below are some typical application examples for each cable tie:
Nylon 66 Cable Tie
- Automotive Industry: PA66 cable ties are used in the automotive industry to secure and bundle cables and pipes inside vehicles. They offer high strength and high-temperature resistance, capable of withstanding the high temperatures and vibrations associated with vehicle operation.
- Aerospace: PA66 cable ties are suitable for securing cables and components in aerospace equipment. They require high heat resistance and high strength, maintaining stability in extreme environments.
- Electrical Equipment: PA66 cable ties are used to secure and bundle cables and wires in electrical equipment. They are suitable for high-temperature and harsh environments, ensuring the safety and stability of electrical systems.
Nylon 6 Cable Ties
- Household Appliances: PA6 cable ties are suitable for securing and bundling cables and wires in household appliances, providing basic fixing functions. They are ideal for environments with moderate temperature and humidity.
- Cable Management: In general cable management and organization, PA6 cable ties are used for indoor applications to keep cables neat and prevent tangling and damage.
- Lightweight Fixing: PA6 cable ties are suitable for applications that do not require high strength, such as securing lightweight items and temporary bundling.
Conclusion
Here is a summary of the differences between Nylon 6 (PA6) and Nylon 66 (PA66) cable ties in a tabular format for reference.
| Property | Nylon 6 (PA6) | Nylon 66 (PA66) |
| Chemical Formula | (C6H11NO)n | (C12H22N2O2)n |
| Structure | Shorter molecular chains, lower crystallinity | Longer molecular chains, higher crystallinity |
| Density | 1.13 g/cm³ | 1.15 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | Approx. 220℃ | Approx. 260℃ |
| Glass Transition Temperature | Approx. 50℃ | Approx. 70℃ |
| Moisture Absorption | Higher, 1.5-3% | Lower, 1-2% |
| Thermal Stability | Lower, with lower melting and glass transition temperatures | Higher, with higher melting and glass transition temperatures |
| Mechanical Performance | Higher elongation at break, good toughness | Higher stiffness and tensile strength |
| Creep Performance | Poor, more deformation under long-term load | Better, maintains shape stability under long-term load |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Excellent |