The locking mechanism of stainless steel cable ties hasn’t been thoroughly explained on the internet yet. However, it’s a subject that carries both technical significance and practical value. Understanding it can greatly enhance the way we utilize these tools. Today, NIKE PLASTIC is here to demystify the locking mechanism of stainless steel cable ties for you, and we will also share some handy tips for their usage.
What Are Stainless Steel Cable Ties
Stainless steel cable ties, as the name implies, are made from stainless steel used to secure, bind, or bundle objects together. Common materials include grades 201, 304, and 316. Unlike plastic ties, they offer greater tensile strength and boast better corrosion resistance, temperature tolerance, and longevity.
In demanding industrial contexts like oil and gas, shipbuilding, and other scenarios that call for high corrosion resistance and strength, stainless steel cable ties are an excellent choice.
The Locking Mechanism of Stainless Steel Cable Ties
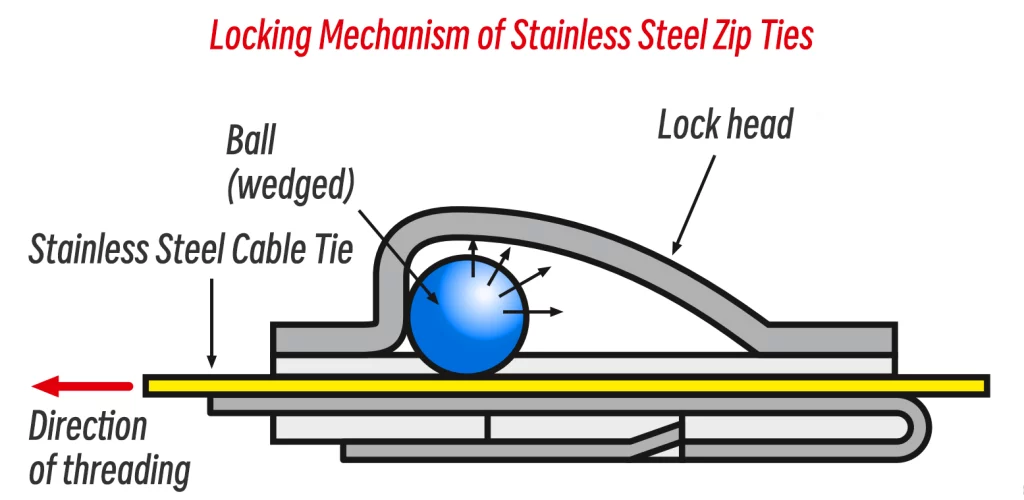
Also known as stainless steel roller ball cable ties, stainless steel cable ties differ from traditional one-piece nylon cable ties. At the heart of their self-locking design is a rolling ball within the buckle. As the tail of the tie is threaded through the head, this ball rolls inward, following the direction of the tie, as illustrated below:
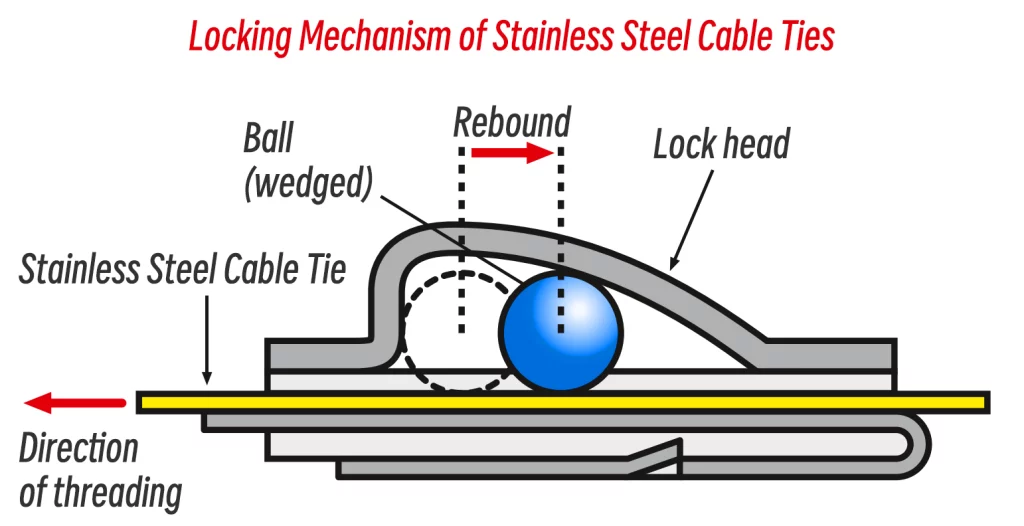
Once tightened to the desired position and released, the tie exerts an outward pull, prompting the ball to roll back slightly and then the ball locks cable ties by wedging, thus securing the tie in place and preventing it from loosening, as shown in the picture below.
How to Use Stainless Steel Cable Ties
Using stainless steel cable ties is quite similar to using the low-profile cable ties found in children’s playgrounds. Just like fastening a belt, you need to thread the tail of the tie straight through the head at 180 degrees and then tighten it. This action is irreversible due to their special structure—the ball-lock design we’ve just described—which leads to a slight retraction after tightening. A pro tip for using these ball-lock ties is to tighten them a bit further than your target position, allowing for this retraction.
In Summary
Understanding the locking mechanism of stainless steel cable ties reveals a potential drawback: they might not adhere as snugly to smooth, non-elastic objects as nylon cable ties, leading to slippage. Thus, choosing the right type of cable tie should be based on our specific needs.